by Tom Minnon, LEED® AP, CDT, Eastern Region Sales Manager for Tubelite Inc.
For the past 20 years, the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) has provided a fair, accurate, and credible rating and labeling system for windows, doors, and skylights used in residential construction. Anyone who has shopped for a residential window has seen a label similar to the one below:
 Ratings on the NFRC label have been achieved through standardized test methods at independently operated laboratories. This standardized method allows you to fairly compare window performance of “Manufacturer A” to “Manufacturer B.”
Ratings on the NFRC label have been achieved through standardized test methods at independently operated laboratories. This standardized method allows you to fairly compare window performance of “Manufacturer A” to “Manufacturer B.”
The NFRC testing protocols involve testing of the full window — including glass, frame, spacers, and any other component that is a permanent part of the complete product. This strategy provides a more accurate reflection of how the product will perform in the home than testing of just glass, as the framing and other components influence ratings such as U-Factor, Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) and Visible Transmittance (VT).
In commercial storefront and curtainwall glazing systems, glazing contractors combine various components that have not been tested as a complete product. For instance, storefront or curtainwall from one manufacturer; glass, coatings and infill from another; and the insulting glass spacer from yet another.
NFRC’s Component Modeling Approach (CMA) Product Certification Program enables whole product energy performance ratings for non-residential projects. CMA uses a simulation tool called CMA Software Tool (CMAST), which includes a database of online performance data for the three primary components of a fenestration product — glazing, frame, and glass spacer — to generate overall product performance ratings for U-Factor, SHGC and VT. The database is essentially a library that houses data on a wide variety of fenestration components. ![Microsoft PowerPoint - EduCode Presentation R2 [Read-Only] [Compatibility Mode]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/EWC_CMA_Diagram.jpg)
While the CMA program has been around for a number of years, it is just now beginning to be widely used and accepted. CMA’s non-residential energy performance data is used in determining code compliance and for meaningful whole building energy analysis. The certification and rating program is credible, simple, cost effective, fair, uniform and useful.
Though the current non-residential program offered by the NFRC Site-Built program provides consistent and reliable energy performance ratings, the CMA program allows for different segments of the fenestration industry to obtain standardized energy performance ratings for fenestration components and component systems including glass, spacers, and frames.
Once tested by an accredited lab, modeled by an Approved Calculation Entity, validated by an approved Inspection Agency, and entered into the CMAST database, these systems reside in electronic libraries that can be easily accessed by those who wish to determine and/or obtain NFRC energy performance ratings (U-Factor, SHGC, VT) for entire window, entrance, storefront, and curtainwall systems.
The libraries are especially useful to architects and builders for:
- Designing envelope/fenestration systems for maximum energy efficiency — whether solar control, energy efficiency, daylighting, or passive solar design
- Comparing the energy performance of different fenestration components and products, and making more informed choices
- Enforcing – related specified performance to installed performance
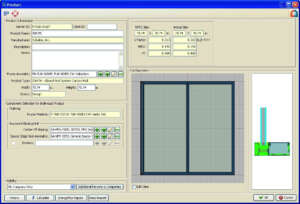
In the example below, the total performance characteristics of the total system are as follows —
- U-Factor: 0.34
- SHGC: 0.20
- VT: 0.43
- LSG: 0.43/0.20 = 2.15 (visible light to solar heat gain)
These values are based on the following components:
- Tubelite’s 400 Series curtainwall with 2.5 x 7.5-inch aluminum framing and thermal pressure plate
- PPG’s Solarban® 70XL low-e glass with 90% argon fill
- Technoform Glass Insulation’s warm edge spacer
CMA shows how changing one component affects overall energy efficiency and provides information on which components can be combined. Ultimately, the information obtained from CMA can be used to determine a whole product energy performance rating for a fenestration system.
Resources:
Efficient Windows Collaborative, http://www.commercialwindows.org/
ENERGY STAR, http://www.energystar.gov
National Fenestration Rating Council, http://www.nfrc.org/
Technoform Glass Insulation, http://www.glassinsulation.us/
Tubelite Inc., http://tubeliteusa.com
**
Tom Minnon, LEED® AP, CDT, is the eastern region sales manager for Tubelite Inc., serving clients from Maine to Georgia. With nearly four decades of industry experience and many professional accreditations, he regularly provides educational and consultative support to architects, buildings owners and glazing contractors regarding storefront, curtainwall, entrances and daylight control systems.
###